Executive Summary
The AI governance landscape is rapidly evolving in 2025, fueled by new regulations and intensifying scrutiny over bias in AI systems. This article explores U.S. federal and California state mandates, cutting-edge bias mitigation strategies, and a governance checklist adapted from Beyond1n0’s AI Risk Management guide and Kamran Iqbal’s audit framework. Designed for executives, it offers actionable steps to integrate fairness into risk management, drive compliance, and maintain stakeholder trust.
Policy & Legal Context: High-Stakes Mandates
🏛 Federal Executive Order on AI Neutrality
In July 2025, the White House issued an executive order requiring federal AI contractors to ensure ideological neutrality in generative models—addressing growing concerns about political and social bias in AI outputs (White House, 2025). This places bias alongside cybersecurity and privacy as a primary governance concern. (wsj.com)
⚖ California’s Judicial AI Regulations
California’s Judicial Council rolled out strict regulations in September 2025, banning generative AI use in certain judicial processes. Citing confidentiality, fairness, and transparency concerns, some courts have opted to block AI tools entirely (Law.com).
These actions solidify ideological bias as the third pillar of AI risk—demanding robust, enforceable governance.
Relatable Bias Risks & Mitigation in Practice
🧠 Hiring Tool Disparities
A June 2025 MIT study found significant demographic disparities in AI-powered hiring platforms (e.g., GPT-4o, Claude 4), with resume-based bias rates as high as 12%. After applying affine concept editing—a model weight-adjustment technique—bias rates dropped to 2.5% (MIT, 2025), showcasing effective mitigation.
🕵️ Prompt Injection & Shadow AI
In 2024, a ChatGPT misuse incident led to a $2M IP leak due to unmonitored “shadow AI” usage. Such tools—like GitHub Copilot or AI chatbots—pose risks if left untracked. The Beyond1n0 AI Risk Management guide recommends enforcing AI inventories and access controls to prevent such incidents.
🧰 Toolkits & Frameworks
Organizations can use frameworks like AI TRiSM, NIST AI RMF, ISO 42001, and Beyond1n0’s checklist to establish layered protections:
Inventory: Identify all AI tools (including unauthorized tools like Copilot).
Risk Assessments: Evaluate fairness, bias, and leakage risks.
Vendor Oversight: Review third-party AI tools for bias and security posture.
Ongoing Audits: Monitor for model drift, prompt misuse, and fairness regression.
Tools like the Aequitas Fairness Toolkit provide open-source solutions for bias audits and equitable outcomes (Aequitas, 2025).
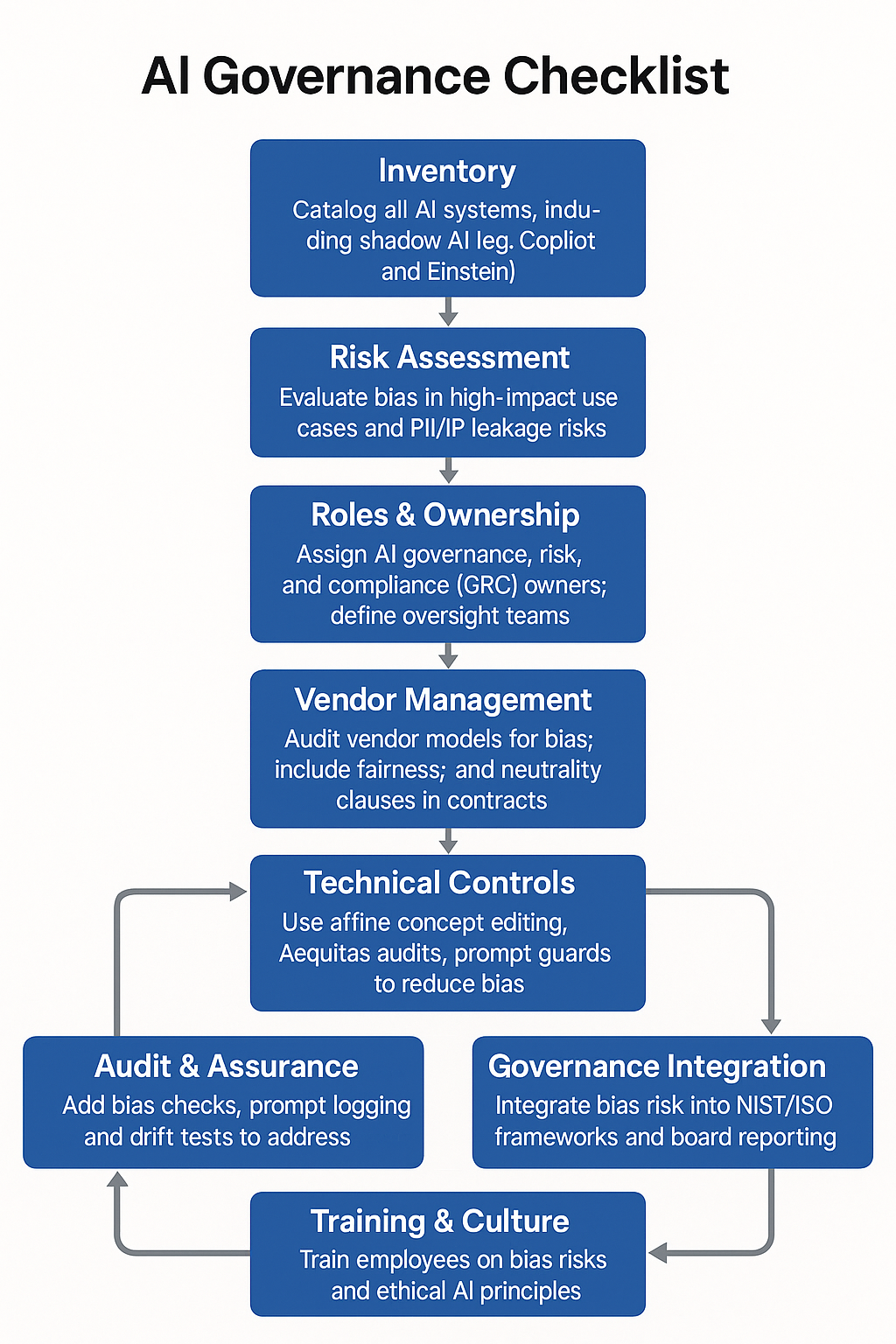
Governance Checklist: A Risk Manager’s Playbook
Adapted from Beyond1n0’s AI Risk Management guide and Kamran Iqbal’s 100-point audit checklist, this framework helps organizations operationalize fairness in AI systems:
| Phase | Key Action |
|---|---|
| Inventory | Catalog all AI tools, including “shadow AI” like Copilot and Einstein. |
| Risk Assessment | Identify bias in high-impact use cases; assess IP/PII leakage risks. |
| Roles & Ownership | Define AI GRC owners and oversight teams across legal, tech, and compliance. |
| Vendor Management | Include neutrality clauses and audit rights in vendor AI contracts. |
| Technical Controls | Apply affine concept editing; run Aequitas audits and prompt security tools. |
| Monitoring | Log prompts; deploy bias drift tests and red-team exercises. |
| Audit & Assurance | Add bias metrics to audit trails; conduct quarterly compliance reviews. |
| Governance Integration | Align with NIST RMF and ISO 42001; report bias risk to executive boards. |
| Training & Culture | Educate staff on bias, fairness, and ethical AI design. |
| Continuous Review | Re-evaluate governance after updates, incidents, or regulatory changes. |
Real-World Examples of Governance in Action
💊 AstraZeneca’s Bias-Reduction Initiative
AstraZeneca adopted a centralized AI governance model in 2024. By applying ethical principles and NIST RMF standards to clinical trial AI systems, the company reduced patient selection bias by 15%—boosting both fairness and regulatory confidence (arXiv, 2025).
📋 Kamran Iqbal’s AI Audit Framework
Iqbal’s 100-point audit checklist offers an actionable framework for aligning AI systems with bias, security, and compliance expectations (AI Governance Library, 2025).
📁 Beyond1n0’s AI Governance Templates
Beyond1n0’s downloadable governance templates accelerate adoption of fair AI practices. Use the “AI Risk Management” guide to support vendor assessments, monitoring, and board-level reporting (Beyond1n0, 2025).
Strategic Recommendations for Executives
Treat Bias as Core Risk: Manage AI bias with the same rigor as cybersecurity or data privacy.
Update Procurement Policies: Require fairness audits and neutrality clauses in vendor contracts.
Apply Technical Controls: Use affine concept editing and Aequitas bias benchmarks.
Establish AI Oversight Councils: Align legal, compliance, tech, and operations leadership.
Enforce Continuous Monitoring: Log prompts, audit AI usage, and implement drift detection.
Train & Communicate: Educate teams and inform boards through regular reporting cycles.
Conclusion
AI bias is a governance imperative in 2025. With expanding regulations and public scrutiny, organizations must embed fairness into risk frameworks now—not later. By integrating legal mandates, technical safeguards, and stakeholder oversight, leaders can ensure compliance, build trust, and protect their brand.
📥 Call-to-Action:
Download Beyond1n0’s AI Risk Management Guide to implement best practices today: